Model T Serial Cable: Difference between revisions
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
have a DTE pinout, the same as a com port on a PC, but with a female connector, unlike a pc. | have a DTE pinout, the same as a com port on a PC, but with a female connector, unlike a pc. | ||
This is a backwards configuration from everything else today. This | This is a backwards configuration from everything else today. This was not always the universal standard, but the universal standard ''today''' and ever since the IBM PC, is that DTE ports (serial ports on host computers) are male (9-pin or 25-pin), and a DB25F (25-pin female) is one of 2 things: it is either a parallel printer port, or a DCE port on a peripheral (like a modem or printer), not a DTE port on a computer. | ||
This means that most serial cables you will find today will need some sort of adapter to connect a "Model T" to anything else | This means that most serial cables you will find today will need some sort of adapter to connect a "Model T" to anything else. | ||
So a single cable with both the right wiring on the inside, and the right connectors on the outside, without needing a stack of adapters, is a little bit special. They do make them, but you just have to search for them specially. Sometimes you can find a cable with that combination of properties by searching for a "Serial Printer" cable. Several known-good ideal cables are linked below. | If you have a null-modem cable, it will probably have female connectors on both ends, and probably will be 9-pin on both ends. You would need either a gender-changer or a 9-to-25 adapter or both to use that. | ||
If you have a cable with the right connectors on both ends (25 pin male and 9 pin femal), it is probably a straight-through "modem" cable, not a null-modem cable. You would need at minimum a male-to-female null-modem adapter to use that. | |||
So a single cable with both the right wiring on the inside, and the right connectors on the outside, without needing a stack of adapters, is a little bit special. They do make them, but you just have to search for them specially. Sometimes you can find a cable with that combination of properties by searching for a "Serial Printer" cable. | |||
Several known-good ideal cables are linked below. | |||
The ideal cable is this: | The ideal cable is this: | ||
| Line 24: | Line 28: | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center; margin: auto;" | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center; margin: auto;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
!colspan="4"|looking at cable end!!rowspan="0"|[[File:RS-232-Null-Modem-Cable-DE9F-to-DB25M.jpg]] | <!-- !colspan="4"|looking at cable end!!rowspan="0"|[[File:RS-232-Null-Modem-Cable-DE9F-to-DB25M.jpg]] --> | ||
!colspan="4"|looking at cable end!!rowspan="0"|[[File:DE9F DB25M.jpg|400px]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
!colspan="2"|female<br>[[File:Conn_dsub9f.gif]]!!colspan="2"|male<br>[[File:Conn_dsub25m.gif]] | !colspan="2"|female<br>[[File:Conn_dsub9f.gif]]!!colspan="2"|male<br>[[File:Conn_dsub25m.gif]] | ||
| Line 36: | Line 41: | ||
| TX || 3 || 3 || RX | | TX || 3 || 3 || RX | ||
|- | |- | ||
| DTR || 4 || 6<br>8 || DSR<br>DCD | | DTR || 4 || 6<br>8 || DSR<br>DCD(note) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| SG || 5 || 7 || SG | | SG || 5 || 7 || SG | ||
| Line 48: | Line 53: | ||
<br clear=all> | <br clear=all> | ||
(note) Model 100 does not have anything connected to the DCD pin, so technically you could omit pin 8 on the 25-pin end of the cable, but the cable itself should still have it just to conform to standards and so there are no mystery surprises when connected to other things. Also perhaps some of the other Model T's besides Model 100 may actually have that pin connected. I haven't checked all models for that detail. | |||
==Ideal Cables== | ==Ideal Cables== | ||
| Line 67: | Line 72: | ||
==Software Flow Control Only Cables== | ==Software Flow Control Only Cables== | ||
These cables are not full-handshake, but | These cables are not full-handshake, but still work fine for almost everything. | ||
They are not ''ideal'' only because the RTS/CTS hardware flow control lines are either missing or faked or wired in some non-standard way. But that is not a major concern because almost nothing uses rts/cts on a Model T. | |||
Software flow-control is the only thing any software ever used on these machines, because the system ROM doesn't contain any code to accesses the RTS/CTS pins. The hardware is present and functional, but can only be accessed from machine language programs. [http://bitchin100.com/wiki/index.php?title=HTERM HTERM] and [https://bitchin100.com/wiki/index.php?title=TBACK TBACK] are the only known examples of that. | |||
These cables have the correct physical plugs, and correct TX/RX wiring, and have DSR/DTR at least faked, and so they work for all software flow-control applications, which is just about everything, including [[TPDD_Emulators|TPDD emulators]]. | |||
Special note about TPDD: TPDD clients all require that the DTR pin be connected to something. It can be faked (shorted to the machine's own DSR), or real (connected to the other ends DSR), or even wierder setups like connecting to RTS+CTS, but it has to be connected to something. A minimal 3-conductor cable can still do TPDD as long as it has DTR shorted to DSR | Special note about TPDD emulators: [https://github.com/bkw777/dlplus/tree/master/clients TPDD clients] all require that the DTR pin be connected to something. It can be faked (shorted to the machine's own DSR), or real (connected to the other ends DSR), or even wierder setups like connecting to RTS+CTS, but it has to be connected to something. A minimal 3-conductor cable can still do TPDD as long as it has DTR shorted to DSR in the DB25 plug. Many generic cables don't have that but these specific cables all do. | ||
*[https://www.monoprice.com/product?p_id=479 Monoprice 479] | *[https://www.monoprice.com/product?p_id=479 Monoprice 479] | ||
| Line 95: | Line 104: | ||
:DSR+CTS<-->DTR | :DSR+CTS<-->DTR | ||
:No RI | :No RI | ||
:This is a very unusual type of cable. If you don't have an HP or IBM plotter, I would not recommend getting this. But, strictly for the TX/RX and the physical connectors, as long as the software is ignoring RTS/CTS and DSR/DTR, it does work, so if you do have an HP or IBM plotter, then you could use this for both your plotter and your M100. | :This is a very unusual type of cable. If you don't have an HP or IBM plotter, I would not recommend getting this. But, strictly for the TX/RX and the physical connectors, as long as the software is ignoring RTS/CTS and DSR/DTR, it does work, so if you do have an HP or IBM plotter, then you could use this for both your plotter and your M100. It is included here simply for completeness and reference, not as a suggestion. | ||
* [https://www.amazon.com/dp/B078M4H4H8 AYA NM9F25M-06] | * [https://www.amazon.com/dp/B078M4H4H8 AYA NM9F25M-06] | ||
:DCD<-->RTS+CTS | :DCD<-->RTS+CTS | ||
| Line 103: | Line 112: | ||
Any one will work well enough. But some considerations are: | Any one will work well enough. But some considerations are: | ||
Models based on FTDI chips are generally better than the ones based on Prolific chips. | Models based on FTDI chips are generally better than the ones based on Prolific or other chips. | ||
Try to get a usb-serial adapter that has nuts, not screws. | Try to get a usb-serial adapter that has nuts, not screws. | ||
Here are a few ideal examples | Here are a few ideal known-good examples. | ||
*[https://www.amazon.com/ | ===USB-C=== | ||
*[https://www.amazon.com/ | *[https://www.amazon.com/dp/B073ZJ6M2X/ Gearmo GM-FTDI2-LED16-C] (FTDI) | ||
*[https://www.amazon.com/gp/product/B074VN9ZG4/ Startech ICUSB232C] (Prolific) | |||
*[https://www.amazon.com/dp/B005SYQV9C/ Sabrent SBT-FTDI] | ===USB=== | ||
*[https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0762BSKGC/ Tera Grande USB2-RS232WN-03] | *[https://www.amazon.com/dp/B005SYQV9C/ Sabrent SBT-FTDI] (FTDI) | ||
*[https://www.amazon.com/dp/B01DT6K8G2/ Gearmo GM-FTDI2-LED] | *[https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0762BSKGC/ Tera Grande USB2-RS232WN-03] (FTDI) | ||
*[https://www.amazon.com/dp/B01DT6K8G2/ Gearmo GM-FTDI2-LED] (FTDI) | |||
*[https://www.amazon.com/dp/B01AT2FTOU/ DTECH DT-5018] (FTDI, has both 9 and 25 pin connectors) | |||
*[https://www.amazon.com/dp/B0007T27H8 TRENDnet TU-S9] (Prolific) | |||
==Legend== | ==Legend== | ||
Latest revision as of 13:20, 17 August 2024
Summary
The ideal cable to go from a PC to a Model 100, 102, 200, or 600, would be described as "9F/25M serial null-modem full-handshake".
That is an uncommon configuration to find in a single cable without needing adapters or needing to build it yourself custom.
The serial ports on
- TRS-80/TANDY Model 100, 102, 200, 600
- NEC PC-8201, PC-8201A, PC-8300, PC-8401 / Starlet, PC-8500
- Olivetti M10
- Kyotronic KC-85
have a DTE pinout, the same as a com port on a PC, but with a female connector, unlike a pc.
This is a backwards configuration from everything else today. This was not always the universal standard, but the universal standard today' and ever since the IBM PC, is that DTE ports (serial ports on host computers) are male (9-pin or 25-pin), and a DB25F (25-pin female) is one of 2 things: it is either a parallel printer port, or a DCE port on a peripheral (like a modem or printer), not a DTE port on a computer.
This means that most serial cables you will find today will need some sort of adapter to connect a "Model T" to anything else.
If you have a null-modem cable, it will probably have female connectors on both ends, and probably will be 9-pin on both ends. You would need either a gender-changer or a 9-to-25 adapter or both to use that.
If you have a cable with the right connectors on both ends (25 pin male and 9 pin femal), it is probably a straight-through "modem" cable, not a null-modem cable. You would need at minimum a male-to-female null-modem adapter to use that.
So a single cable with both the right wiring on the inside, and the right connectors on the outside, without needing a stack of adapters, is a little bit special. They do make them, but you just have to search for them specially. Sometimes you can find a cable with that combination of properties by searching for a "Serial Printer" cable.
Several known-good ideal cables are linked below.
The ideal cable is this:
| looking at cable end | 
| |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
female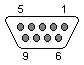 |
male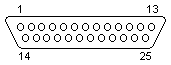
| |||
| DTE | DTE | |||
| Signal | DE9F | DB25M | Signal | |
| RX | 2 | 2 | TX | |
| TX | 3 | 3 | RX | |
| DTR | 4 | 6 8 |
DSR DCD(note) | |
| SG | 5 | 7 | SG | |
| DSR DCD |
6 1 |
20 | DTR | |
| RTS | 7 | 5 | CTS | |
| CTS | 8 | 4 | RTS | |
(note) Model 100 does not have anything connected to the DCD pin, so technically you could omit pin 8 on the 25-pin end of the cable, but the cable itself should still have it just to conform to standards and so there are no mystery surprises when connected to other things. Also perhaps some of the other Model T's besides Model 100 may actually have that pin connected. I haven't checked all models for that detail.
Ideal Cables
These cables are wired null-modem, have all the connections for hardware flow-control, and the right physical connectors on both ends, all in one factory-molded piece. You don't need any null-modem adapters or gender-changer adapters.
- No RI
- S+PG
- No RI
- S+PG
- No RI
- Includes nuts (removable) on the 9-pin plug screws, so if you have the wrong kind of usb-serial adapter you can still screw it to the cable.
- No DCD
- No RI
Software Flow Control Only Cables
These cables are not full-handshake, but still work fine for almost everything.
They are not ideal only because the RTS/CTS hardware flow control lines are either missing or faked or wired in some non-standard way. But that is not a major concern because almost nothing uses rts/cts on a Model T.
Software flow-control is the only thing any software ever used on these machines, because the system ROM doesn't contain any code to accesses the RTS/CTS pins. The hardware is present and functional, but can only be accessed from machine language programs. HTERM and TBACK are the only known examples of that.
These cables have the correct physical plugs, and correct TX/RX wiring, and have DSR/DTR at least faked, and so they work for all software flow-control applications, which is just about everything, including TPDD emulators.
Special note about TPDD emulators: TPDD clients all require that the DTR pin be connected to something. It can be faked (shorted to the machine's own DSR), or real (connected to the other ends DSR), or even wierder setups like connecting to RTS+CTS, but it has to be connected to something. A minimal 3-conductor cable can still do TPDD as long as it has DTR shorted to DSR in the DB25 plug. Many generic cables don't have that but these specific cables all do.
- DCD<-->RTS+CTS
- RI<-->RI
- DCD<-->RTS+CTS
- RI<-->RI
- DCD<-->RTS+CTS
- No RI
- DCD<-->RTS+CTS
- No RI
- DTR<-->DCD+RTS+CTS
- No RI
- DTR<-->DCD+RTS+CTS
- No RI
- DCD<-->RTS
- DSR+CTS<-->DTR
- No RI
- This is a very unusual type of cable. If you don't have an HP or IBM plotter, I would not recommend getting this. But, strictly for the TX/RX and the physical connectors, as long as the software is ignoring RTS/CTS and DSR/DTR, it does work, so if you do have an HP or IBM plotter, then you could use this for both your plotter and your M100. It is included here simply for completeness and reference, not as a suggestion.
- DCD<-->RTS+CTS
- RI<-->RI
USB-Serial Adapters
Any one will work well enough. But some considerations are:
Models based on FTDI chips are generally better than the ones based on Prolific or other chips.
Try to get a usb-serial adapter that has nuts, not screws.
Here are a few ideal known-good examples.
USB-C
- Gearmo GM-FTDI2-LED16-C (FTDI)
- Startech ICUSB232C (Prolific)
USB
- Sabrent SBT-FTDI (FTDI)
- Tera Grande USB2-RS232WN-03 (FTDI)
- Gearmo GM-FTDI2-LED (FTDI)
- DTECH DT-5018 (FTDI, has both 9 and 25 pin connectors)
- TRENDnet TU-S9 (Prolific)
Legend
For all the cable wiring notes above, the notes indicate how the cable differs from a canonical RS-232 DTE-to-DTE null-modem reference.
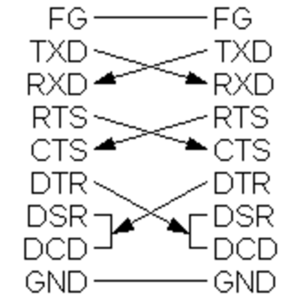
Any signal that is not mentioned, is wired according to the reference. IE, if TX or RX is not mentioned, then TX on one end of the cable is connected to RX on the other end of the cable.
Unless otherwise noted, the indicated wiring is symmetrical, the indicated connections are the same on both ends of the cable.
S+PG
- The cable Shield (& connector shell) is connected to Protective Ground or "frame ground" (pin 1 on the DB25 connector, no pin on the DB9 just the connector shell)
RI<-->RI
- Ring Iindicator is connected to Ring Indicator
- DB25 pin 22 (RI) is connected to DE9 pin 9 (RI)
DCD<-->RTS+CTS
- Request To Ssend is connected to Clear T Send on one end, and both are connected to Data Carrier Detect on the other end.
- DB25 pins 4 (RTS) & 5 (CTS) are connected to each other, and to DE9 pin 1 (DCD).
- DE9 pins 7 (RTS) & 8 (CTS) are connected to each other, and to DB25 pin 8 (DCD).