TPDD: Difference between revisions
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
Software related to these drives can be broken into 2 main categories, [[TPDD_client|clients]] and [[TPDD_server|servers]]. | Software related to these drives can be broken into 2 main categories, [[TPDD_client|clients]] and [[TPDD_server|servers]]. | ||
A [[TPDD_client | A [[TPDD_client]] (or DOS) is software that uses a TPDD drive. This includes the "Floppy" that came on the utility disk that came with the drive, TS-DOS, and others. | ||
A [[ | A [[TPDD_server]] (or emulator) is software that pretends to BE a TPDD drive. This includes LaddieAlpha, dlplus, and others. | ||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
==For "Model T"s== | ==For "Model T"s== | ||
Revision as of 04:44, 31 July 2021
Tandy Portable Disk Drive
There were two versions of the Tandy Portable Disk Drive, "26-3808 Tandy Portable Disk Drive" or "TPDD1", and "26-3814 Tandy Portable Disk Drive 2" or "TPDD2". Both were very similar. The original TPDD1 is a re-branded Brother FB-100.
Common features of both versions
- Size, shape, weight
- Batteris: 4 x AA
- Wall power: 5.5mm x 2.1mm, 6vdc, center negative, 400ma (Tandy 26-3804)
- Media: 3.5" DD, aka "720K" diskettes (not HD 1.44M)
- Drive is single-sided. The disks may be single or double-sided, but the drive only uses one side.
Documentation
Tandy Portable Disk Drive
100K
Tandy Portable Disk Drive 2
200K, in the form of 2 100K banks
Parts
Belt
Standard size code: FRW-8.5
Search "FRW 8.5 belt" on Google or ebay
Cable
The "RS-232C" interface to the TPDD is actually 5v TTL (0v to +5v), while RS-232 serial ports use -12v to +12v. So the cable isn't just a cable, it has electronics inside the DB25 plug to convert the signal levels between TTL and RS-232.
Pinout
+------------------------------------------------+ | | | | | RS-232C | | ___ | | +--+ +--+ +-----+ | | | 7 5 3 1 | | (o) | | | | 8 6 4 2 | | | | | +---------+ +-----+ | +------------------------------------------------+
- 1 GND
- 2 CTS
- 3 DTR
- 4 RTS
- 5 DSR
- 6 TXD
- 7 RXD
- 8 EB+ (External Battery +4.8 to +6v)
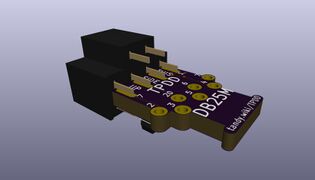
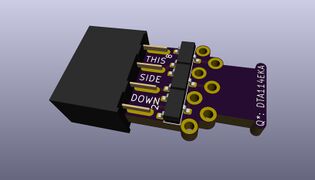
KiCAD source for schematic & pcb to build a cable
- Assembly:
- Solder all components to pcb per the render pics.
- Pull the two un-soldered pins from the top of the socket and discard.
- Cut the 9-pin plug off the serial cable. Strip the outer sheath back 1 to 2 inches. Strip each wire 1/8".
- Put 2 to 3 inches of 1/2" diameter heat shrink on the serial cable. (don't shrink yet)
- Identify which color wires go to which pins on the DB25 plug.
- Find pin 2 on the db25
- Find which color wire goes to pin 2 using a DMM continuity tester
- Repeat for all the numbered holes on the PCB: 2,3,4,5,6,7,20
- Cut any left-over wires short right at the cable sheath.
- Solder the wires to their matching numbered holes, with the wires on the top side (without the transistors).
- Put some hot-glue on the top side of the pcb in the "dog bone", press the end of the cable into the glue, and secure to the pcb with a zip-tie.
- Add some hot-glue around the soldered wires where they meet the pcb to immobilize them.
- Slide the heat-shrink up over the pcb and shrink.
Software
Software related to these drives can be broken into 2 main categories, clients and servers.
A TPDD_client (or DOS) is software that uses a TPDD drive. This includes the "Floppy" that came on the utility disk that came with the drive, TS-DOS, and others.
A TPDD_server (or emulator) is software that pretends to BE a TPDD drive. This includes LaddieAlpha, dlplus, and others.